Bartholin's cyst is a condition in which inflammation occurs at the entrance of the vulva and vagina. In this article, frequently asked questions about bartholin's cyst, which is an abscess caused by sexually transmitted diseases; We wanted to inform you in line with the questions asked by my patients.
Table of Contents
What is a Bartholin’s Cyst?
Bartholin's glands are glands located on both sides of the vaginal opening (vaginal lips). In case of obstruction of the liquid-filled bartholin glands, which keep the vagina moist, provide lubricity during sexual intercourse, swelling occurs and this causes a bartholin cyst (abscess).
Bartholin's cysts;
- It is soft textured.
- It appears as a lump.
- It is generally benign.
- It is not a cancer cell.
What Are the Symptoms of a Bartholin’s Cyst?
Bartholin's cyst presents with swelling of the infected gland. Bartholin's abscess;
- A tender, painful lump at the entrance to the vagina or near the outer lips of the vagina
- while walking or while sitting discomfort
- pain during intercourse
- Fire
It may show signs.
If you have a small or not yet infected Bartholin's cyst, you may not notice it. If the cyst enlarges, you may feel a lump, a mass at the entrance to the vagina or near the outer lips of the vagina.
Although Bartholin's abscess is usually seen on the unilateral outer lip, it can rarely be seen on both lips of the vagina.
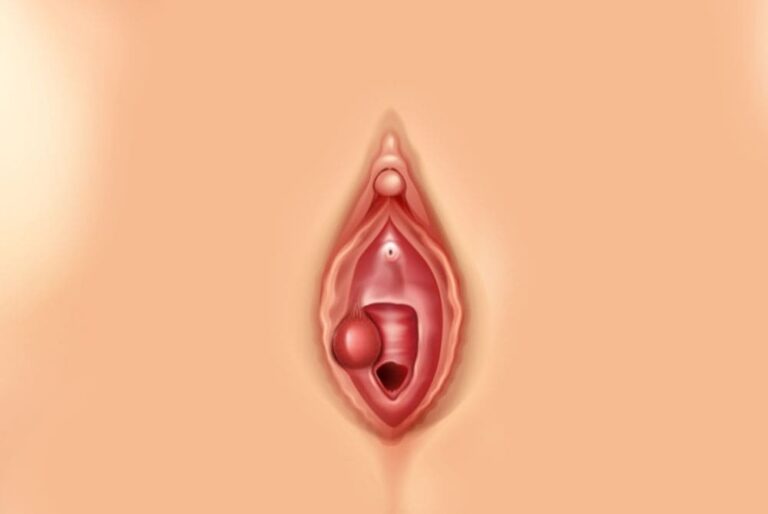
Why Does a Bartholin’s Cyst Occur?
“Why Does a Bartholin Cyst Occur?” of the question The answer is blockage of the bartholin's glands. Causes of obstruction of Bartholin glands;
- Infections that can cause abscesses,
- sexually transmitted diseases such as chlamydia, gonorrhea, Escherichia coli (a type of bacteria also known as coli bacillus),
- Rarely, disruption of the vaginal flora
It can be sorted as
Disruption of the vaginal flora also causes vaginal discharge and itching .
Does Experiencing Frequent Sexual Coexistence Cause Bartholin’s Cyst?
Bartholin glands; It produces fluids that provide lubrication so that intercourse can be easy during sexual intercourse. These fluids pass from the bartholin gland through small tubes called ducts and move towards the vagina. If the ducts become blocked, they can fill with fluid and expand, causing an abscess.
Experiencing frequent sexual intercourse may cause obstruction in the ducts with the increase of the fluid in the bartholin glands. However, we cannot say exactly what causes frequent sexual intercourse . sexually transmitted diseases such as chlamydia, gonorrhea, coli; is the root cause of abscess.
Can I Prevent Bartholin Cyst Formation?
A way to prevent the formation of Bartholin's cyst ; It can be possible with safe sexual intercourse, which is one of the ways to prevent other vaginal diseases. Not only for bartholin's cyst; The way to prevent infections such as chlamydia, gonorrhea and coli bacilli is to use condoms.
How is Bartholin’s Cyst Diagnosed?
It may go unnoticed until the Bartholin's glands become infected and cause swelling. Pelvic examination after Bartholin's cyst occurs, with cervical screening test gynecology diagnosed by your specialist. At the same time, procedures such as smear test can be applied for the diagnosis of sexually transmitted diseases. In some cases, a biopsy is rarely required for the diagnosis of vulvar cancer .
When Should I See a Gynecologist?
If you have a painful lump near your vaginal entrance or on the outer lips of the vagina that does not heal after two or three days, you should make an appointment with your gynecologist.
Although Bartholin's cyst is rarely seen in women over the age of 40; If seen, it may also be a sign of the presence of malignant cells.
How is a Bartholin’s Cyst Treated?
If you do not have symptoms such as pain or tenderness, fever, which we describe in the symptoms of Bartholin's cyst your treatment it may be simple.
If the cyst is painful, your gynecologist may first apply instant treatments such as keeping the cyst in warm water several times a day for 3 or 4 days, painkillers, antibiotics.
If these do not work, several treatments are available to treat the pain and any infection. If necessary, the infected abscess can be drained. Most of these treatments involve minor surgical procedures.
Bartholin's cyst sometimes may recur after treatment.
In the treatment of Bartholin's cyst;
- If the cyst becomes infected and an abscess develops, infection clear Your gynecologist may prescribe antibiotics.
- In some cases, a surgical drainage method known as catheter insertion or fistulization, a procedure used to drain fluid from an abscess or cyst with balloon catheterization, may be performed.
- Surgery to remove the affected Bartholin gland may be recommended by your gynecologist if other treatments have not been effective and your Bartholin cysts have recurred.
- A carbon dioxide laser can be used to create an opening in the skin of the outer labia minora of the vagina so that the cyst can be drained.
- Bartholin's abscess can be drained with needle aspiration.
Considerations After Bartholin’s Cyst Treatment
To reduce the possibility of recurrence due to the presence of openings in the vagina that are more prone to infection after treatment;
- abstain from sexual intercourse for up to 4 weeks
- Not using tampons during menstrual periods
- Staying away from intim products that may disrupt the vaginal flora for up to 4 weeks (if possible, completely avoiding intim products for vaginal hygiene)
- Paying attention to the hygiene of the abscess area treated for 24 to 48 hours after the treatment methods that require general anesthesia, in line with the guidance of your gynecologist.
Required.
CLICK to make an appointment for Bartholin's Cyst .
